CCNA3 v6.0 Chapter 10 Exam Answers
1. A network administrator has just changed the router ID on a router that is working in an OSPFv2 environment. What should the administrator do to reset the adjacencies and use the new router ID?
Configure the network statements.
Change the interface priority.
Issue the clear ip ospf process privileged mode command.*
Change the OSPFv2 process ID.
2. Refer to the exhibit.
What three conclusions can be drawn from the displayed output? (Choose three.)
The DR can be reached through the GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface.*
This interface is using the default priority.
The BDR has three neighbors.
The router ID on the DR router is 3.3.3.3
The router ID values were not the criteria used to select the DR and the BDR.*
There have been 9 seconds since the last hello packet sent.*
3. Refer to the exhibit.
Which conclusion can be drawn from this OSPF multiaccess network?
When a DR is elected all other non-DR routers become DROTHER.
All DROTHER routers will send LSAs to the DR and BDR to multicast 224.0.0.5.
If the DR stops producing Hello packets, a BDR will be elected, and then it promotes itself to assume the role of DR.
With an election of the DR, the number of adjacencies is reduced from 6 to 3.*
4. Which OSPF feature allows a remote OSPF area to participate in OSPF routing when it cannot connect directly to OSPF Area 0?
NBMA
DR/BDR
virtual link*
point-to-point connectivity
5. Refer to the exhibit.
What are three resulting DR and BDR elections for the given topology? (Choose three.)
R3 is BDR for segment A.
R1 is DR for segment A.*
R2 is BDR for segment A.*
R3 is DR for segment A.
R4 is BDR for segment B.
R5 is BDR for segment B.*
6. When checking a routing table, a network technician notices the following entry:
O*E2 0.0.0.0/0 [110/1] via 192.168.16.3, 00:20:22, Serial0/0/0
What information can be gathered from this output?
This route is a propagated default route.*
The route is located two hops away.
The metric for this route is 110.
The edge of the OSPF area 0 is the interface that is addressed 192.168.16.3.
7. Refer to the exhibit.
What two conclusions can be drawn based on the output of the show ipv6 route command? (Choose two.)
Route 2001:DB8:CAFE:4::/64 is an external route advertised by an ASBR.
R2 receives default route information from another router.*
Route 2001:DB8:CAFE:B001::/64 is a route advertised by an ABR.*
Route 2001:DB8:CAFE:4::/64 is advertised by a router three hops away.
Routes 2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64 and 2001:DB8:CAFE:3::/64 are advertised from the same router.
8. Which command will a network engineer issue to verify the configured hello and dead timer intervals on a point-to-point WAN link between two routers that are running OSPFv2?
show ip ospf neighbor
show ip ospf interface serial 0/0/0*
show ipv6 ospf interface serial 0/0/0
show ip ospf interface fastethernet 0/1
9. A network engineer suspects that OSPFv3 routers are not forming neighbor adjacencies because there are interface timer mismatches. Which two commands can be issued on the interface of each OSFPv3 router to resolve all timer mismatches? (Choose two.)
no ipv6 ospf hello-interval*
no ipv6 ospf dead-interval*
ip ospf hello-interval 10
ip ospf dead-interval 40
no ipv6 ospf cost 10
no ipv6 router ospf 10
10. A network engineer has manually configured the hello interval to 15 seconds on an interface of a router that is running OSPFv2. By default, how will the dead interval on the interface be affected?
The dead interval will now be 15 seconds.
The dead interval will now be 30 seconds.
The dead interval will now be 60 seconds.*
The dead interval will not change from the default value.
11. Which command can be used to view the OSPF hello and dead time intervals?
show ip protocols
show ip ospf neighbor
show ip ospf interface*
show ip ospf route
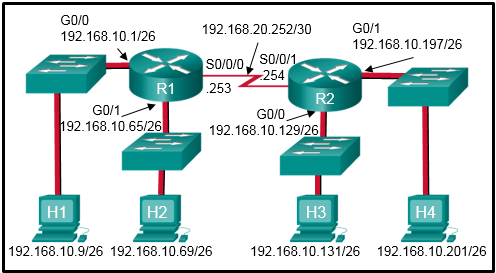
12. Refer to the exhibit.
A network administrator is configuring OSPF for R1 and R2, but the adjacency cannot be established. What is the cause of the issue?
The process ID is misconfigured.
The area ID is misconfigured.*
The IP address on router R2 is misconfigured.
The interface s0/0/0 on router R2 is missing a link-local address.
13. Refer to the exhibit.
What the amount of time that has elapsed since the router received a hello packet?
40 seconds
10 seconds
4 seconds*
6 seconds
14. Which two parameters must match between neighboring OSPF routers in order to form an adjacency? (Choose two.)
hello / dead timers*
process ID
router ID
IP address
network types*
cost
15. Refer to the exhibit.
A network administrator has configured OSPFv2 on the two Cisco routers but PC1 is unable to connect to PC2. What is the most likely problem?
Interface S0/0 is configured as a passive-interface on router R2.
Interface s0/0 has not been activated for OSPFv2 on router R2.
Interface Fa0/0 is configured as a passive-interface on router R2.
Interface Fa0/0 has not been activated for OSPFv2 on router R2.*
16. Refer to the exhibit.
R1 and R2 are connected to the same LAN segment and are configured to run OSPFv3. They are not forming a neighbor adjacency. What is the cause of the problem?
The IPv6 addresses of R1 and R2 are not in the same subnet.
The OSPFv3 process IDs of R1 and R2 are different.
The timer intervals of R1 and R2 do not match.*
The priority value of both R1 and R2 is 1.
17. A network administrator is troubleshooting an OSPFv3 configuration on an IPv6 network. The administrator issues the show ipv6 protocols command. What is the purpose for this command?
to verify OSPFv3 configuration information*
to display the OSPFv3 learned routes in the routing table
to display the OSPFv3 parameters configured on an interface
to verify that the router has formed an adjacency with its neighboring routers
18. Refer to the exhibit.
Directly connected networks configured on router R1 are not being shared with neighboring routers through OSPFv3. What is the cause of the issue?
IPv6 OSPF routing is not enabled.
There is a mismatch of OSPF process ID in commands.*
The no shutdown command is missing on the interfaces.
There are no network statements for the routes in the OSPF configuration.
19. An administrator is troubleshooting OSPFv3 adjacency issues. Which command would the administrator use to confirm that OSPFv3 hello and dead intervals are matching between routers?
show ipv6 ospf interface*
show ipv6 ospf
show ipv6 protocols
show ipv6 ospf neighbor
20. What three states are transient OPSF neighbor states that indicate a stable adjacency is not yet formed between two routers? (Choose three.)
full
exstart*
2way
exchange*
loading*
established
21. Match each OSPF election criterion to its sequential order for the OSPF DR and BDR election process. (Not all options are used.)
22. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Which routers are the DR and BDR in this topology?
DR:R1 BDR:R2
DR:R6 BDR:R5
DR:R5 BDR:R3
DR:R3 BDR:R6
DR:R4 BDR:R1
DR:R3 BDR:R5*
23. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
A network administrator is configuring multiarea OSPFv3 on the routers. The routing design requires that the router RT1 is a DROTHER for the network in Area 0 and the DR for the network in Area 1. Check the settings and status of the routers. What can the administrator do to ensure that RT1 will meet the design requirement after all routers restart?
Restart all routers except for RT1.
Change the router ID to 5.5.5.5 on RT1.
Configure the loopback 0 interface with 6.6.6.6.
Use the ipv6 ospf priority 0 command on the interface g0/0 of RT1.
Use the ipv6 ospf priority 10 command on the interface g0/2 of RT1.*